Process division of cell stock illustration Illustration of bacteria Biology Diagrams Learn how cells divide to make new cells for growth, repair, and sexual reproduction. Explore the differences between mitosis and meiosis, the phases of the cell cycle, and the role of cyclins and centrioles.
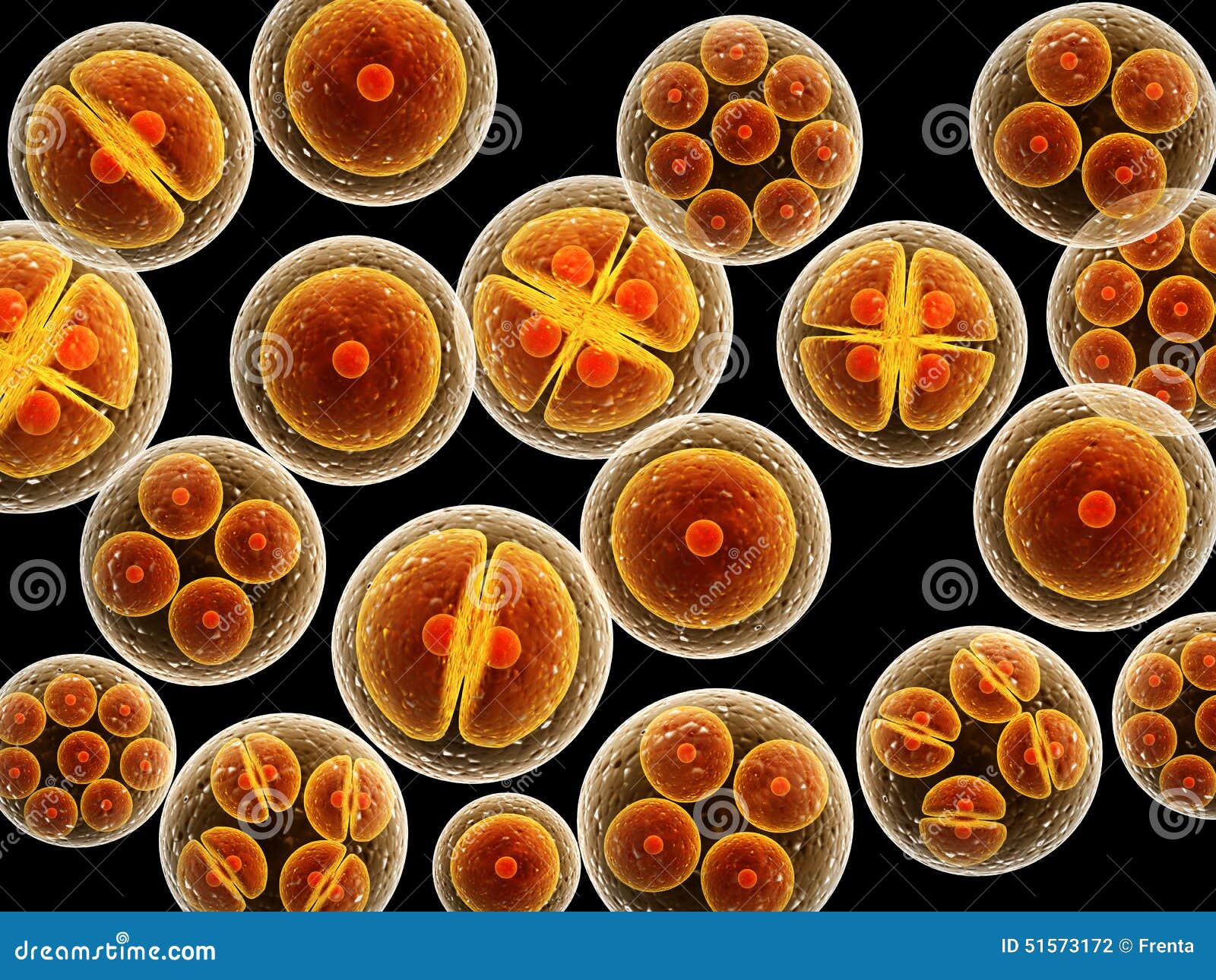
Cell division is a fundamental process that is important for the growth and development of living organisms. Cell division takes place through two processes: Mitosis and Meiosis. Mitosis cell division involves the duplication of the genetic material and the segregation of the cell into two identical daughter cells. This process is essential for

Definition, Types, Mitosis, Meiosis, Cell cycle Biology Diagrams
Cytokinesis is the final act of cell division, bridging the culmination of mitosis or meiosis with the formation of distinct daughter cells. This process involves the division of the cell's cytoplasm, ensuring that each new cell inherits a complete set of chromosomes and a fair distribution of organelles and cellular components.

Learn what cell division is and how it occurs in eukaryotes and prokaryotes. Find out the functions and importance of cell division for living organisms. Learn about the process of cell division, which is essential for growth, repair, and reproduction in living organisms. Explore the different types of cell division, such as binary fission, mitosis, and meiosis, and their functions, phases, and significance.

Mitosis and Meiosis Biology Diagrams
Learn about the two types of cell division (mitosis and meiosis) and the phases of the cell cycle (interphase and M phase) with notes and examples. Test your knowledge with a quiz on cell division by BYJU'S. Learn about the two types of cell division: mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis makes new body cells, while meiosis creates egg and sperm cells for reproduction.
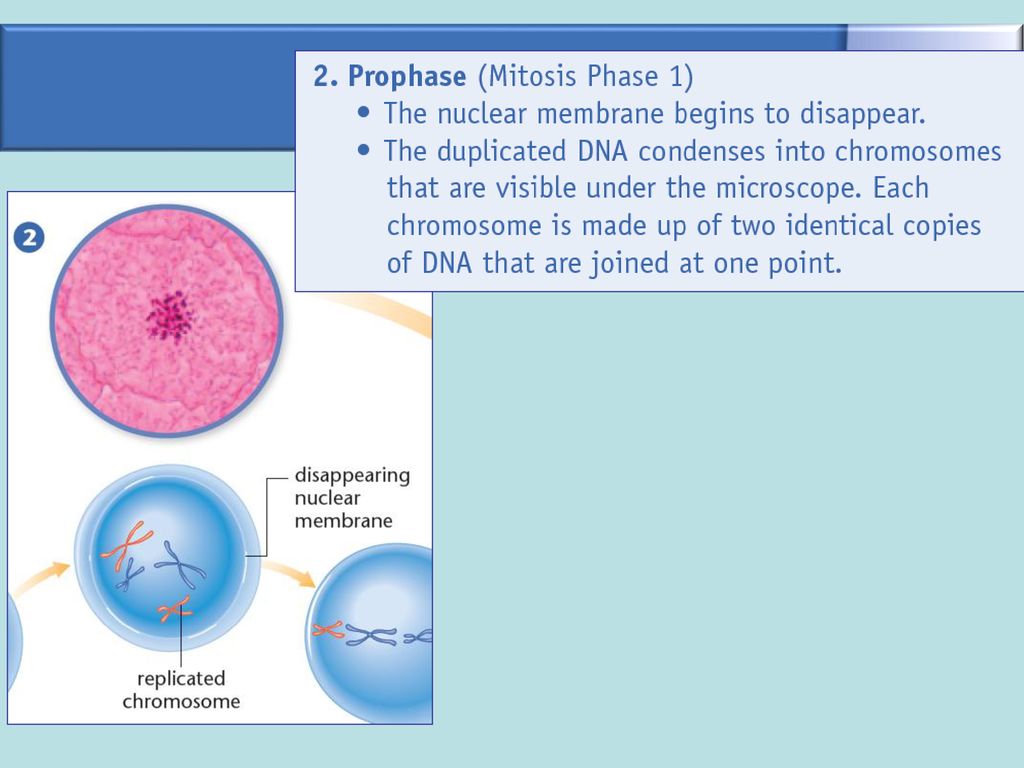
Learn about the process of cell division in prokaryotes and eukaryotes, including mitosis, meiosis, and binary fission. Find out how cell division is regulated, monitored, and controlled by various factors and checkpoints.
