Food Chains TERRESTRIAL ECOSYSTEM FOOD CHAIN Biology Diagrams A food web is made up of all of the interrelated and overlapping food chains in an ecosystem. ⫸ Types of Food Chain. urbanization, and conversion of land for agriculture destroy habitats and fragment ecosystems, severing links in food chains. Pollution: Chemicals, toxins, and heavy metals introduced into the environment can bioaccumulate Activity 3: Farm Food Chains. Prior to this activity, prepare a food chain model by attaching the Food Chain Model Pictures to the plastic cups. Use the food chain model to explain the following points: A food chain is a series of organisms that are each dependent on the next as a food source. A food chain shows how energy moves through an
The complex relationships in ecosystems are shown through food chains and food webs, which are important for understanding how ecosystems work. Food chains show a simple line of energy transfer, showing how each organism has a place, starting with producers that use sunlight and moving up to consumers that get energy from eating. The Importance of Food Chains and Webs in Ecosystem Stability. Both food chains and food webs are integral to the functioning of ecosystems. They regulate populations, maintain balance, and help in nutrient cycling. Agriculture: Understanding pest species and their natural predators can help in pest management and sustainable agriculture This type of food chain ensures maximum utilization and minimum wastage of the available material. It is useful in fixation of inorganic nutrients and utilizing up to the maximum. For example, the food chain operating in the decomposing accumulated litter in a temperate forest ecosystem is a detritus food chain (Fig. 5.2).

Food chain and ecological resources Biology Diagrams
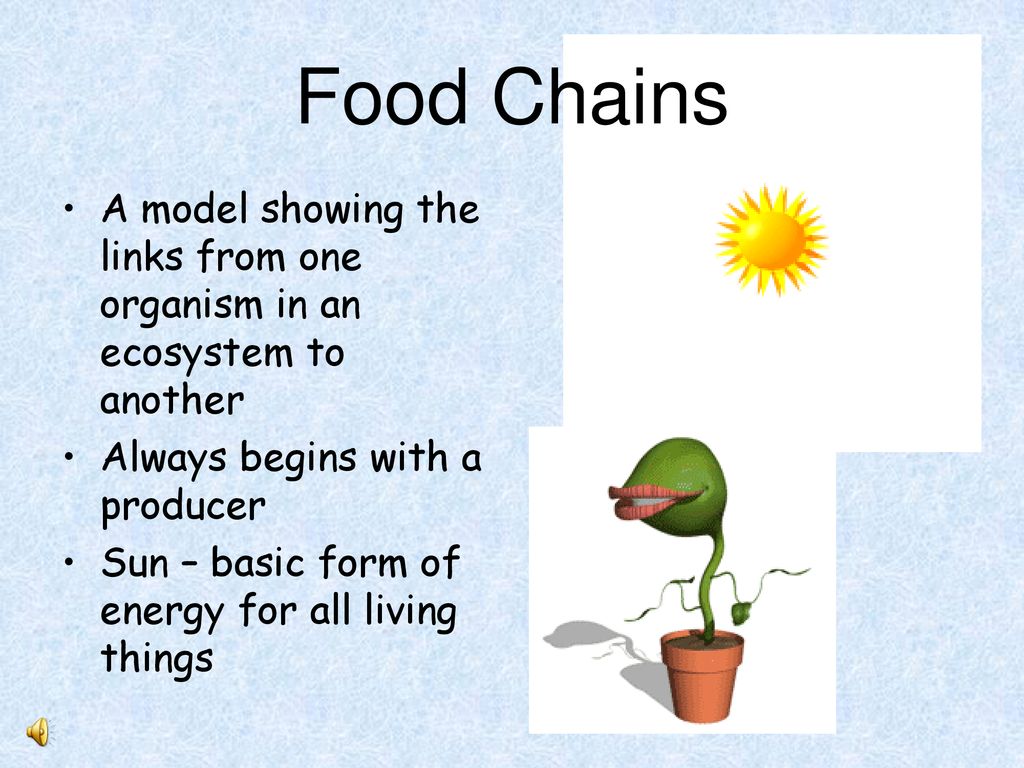
Food chains and food webs are fundamental concepts in ecology that illustrate how energy and nutrients flow through ecosystems. A food chain is a linear representation of feeding relationships, showing how energy moves from one organism to another, while a food web consists of multiple interconnected food chains, reflecting the complex interactions within a community.
3. Dynamics of Food Chains. Food chains are dynamic systems influenced by various factors: Energy Transfer: Energy flows through a food chain in a unidirectional manner, with each trophic level capturing only a fraction of the energy from the previous level. Trophic Levels: Organisms occupy specific trophic levels based on their position in the food chain, with energy decreasing as it moves up Agricultural food webs describe the intricate feeding relationships among various organisms within farming ecosystems. These webs start with primary producers, such as crops and plants that farmers grow. Herbivorous insects, rodents, and other animals that munch on these crops are the primary consumers. Next in line are the secondary consumers.
