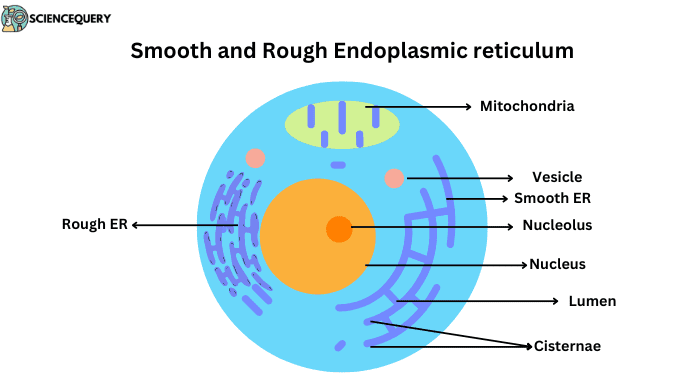
Explain the Endoplasmic reticulum with its types and functions Biology Diagrams The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a vast network of interconnected tubules and flattened sacs within the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. It serves as a key organelle responsible for the synthesis, folding, and transport of proteins, as well as the production and regulation of lipids and other cellular components.
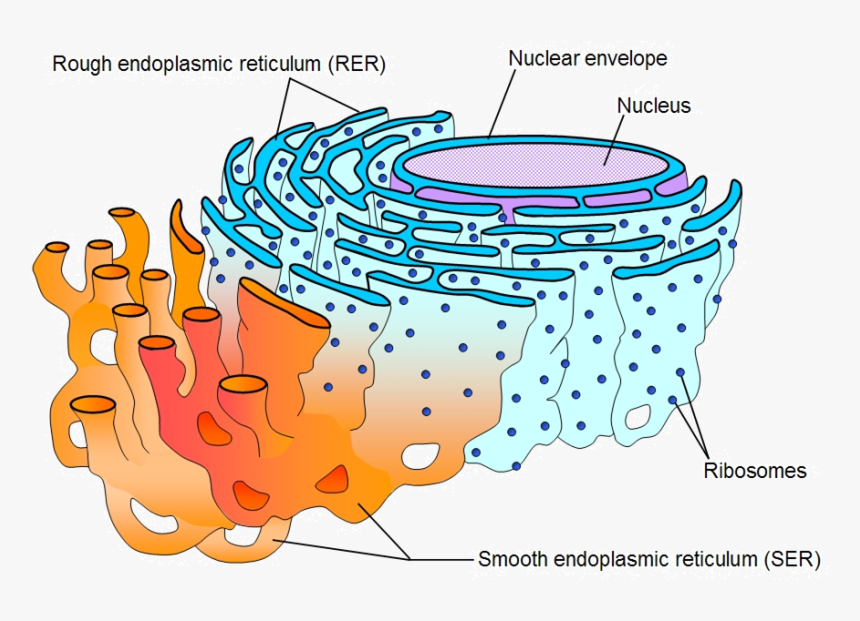
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a part of a transportation system of the eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding.The word endoplasmic means "within the cytoplasm", and reticulum is Latin for "little net". It is a type of organelle made up of two subunits - rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER), and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER). The ER can be classified in two functionally distinct forms: smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) and rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER). The morphological distinction between the two is the presence of protein-synthesizing particles, called ribosomes, attached to the outer surface of the RER.The functions of the SER, a meshwork of fine tubular membrane vesicles, vary considerably from cell to
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/endoplasmic_reticulum-56cb365f3df78cfb379b574e.jpg)
EBSCO Research Starters Biology Diagrams
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is the largest single membrane bound intracellular organelle found in eukaryotic cells that forms an extensive interconnected network of close and flattened membrane sacs or tube-like structures known as cisternae, mainly responsible for synthesis and transport of protein and lipid, metabolism of carbohydrate, compartmentalization of nucleus etc.
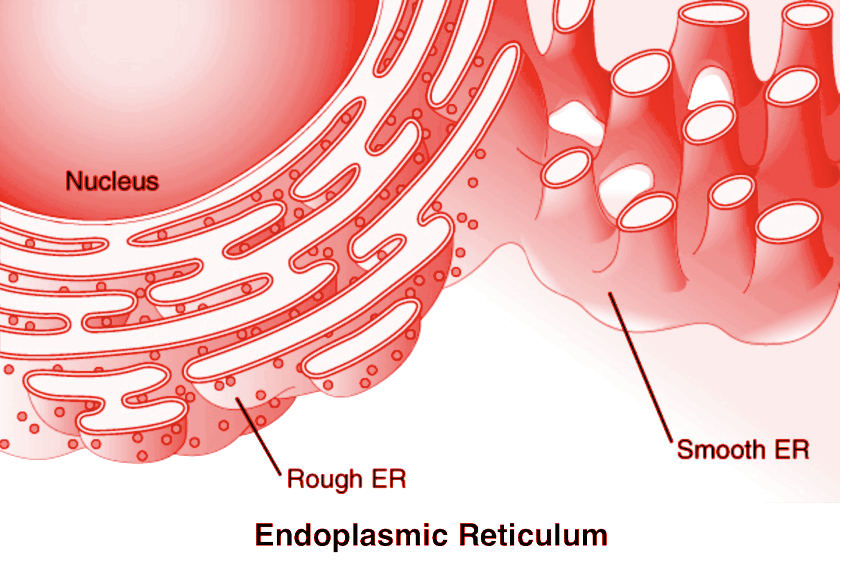
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) consists of a membranous network that extends through the cytoplasm and is continuous with the outer nuclear membrane. Thus, the ER lumen is continuous with the perinuclear space. The ER is divided into the smooth ER (sER) and the rough ER (rER), with the latter having ribosomes attached to the cytoplasmic surface.
Endoplasmic Reticulum; Structure, Types and Functions Biology Diagrams
Endoplasmic Reticulum Diagram. The below diagram shows the variants of the endoplasmic reticulum: Rough ER; Smooth ER; Rough endoplasmic reticulum has ribosomes embedded within its structure, giving a "rough" appearance. The smooth endoplasmic reticulum does not have these ribosomes, hence appearing "smooth."
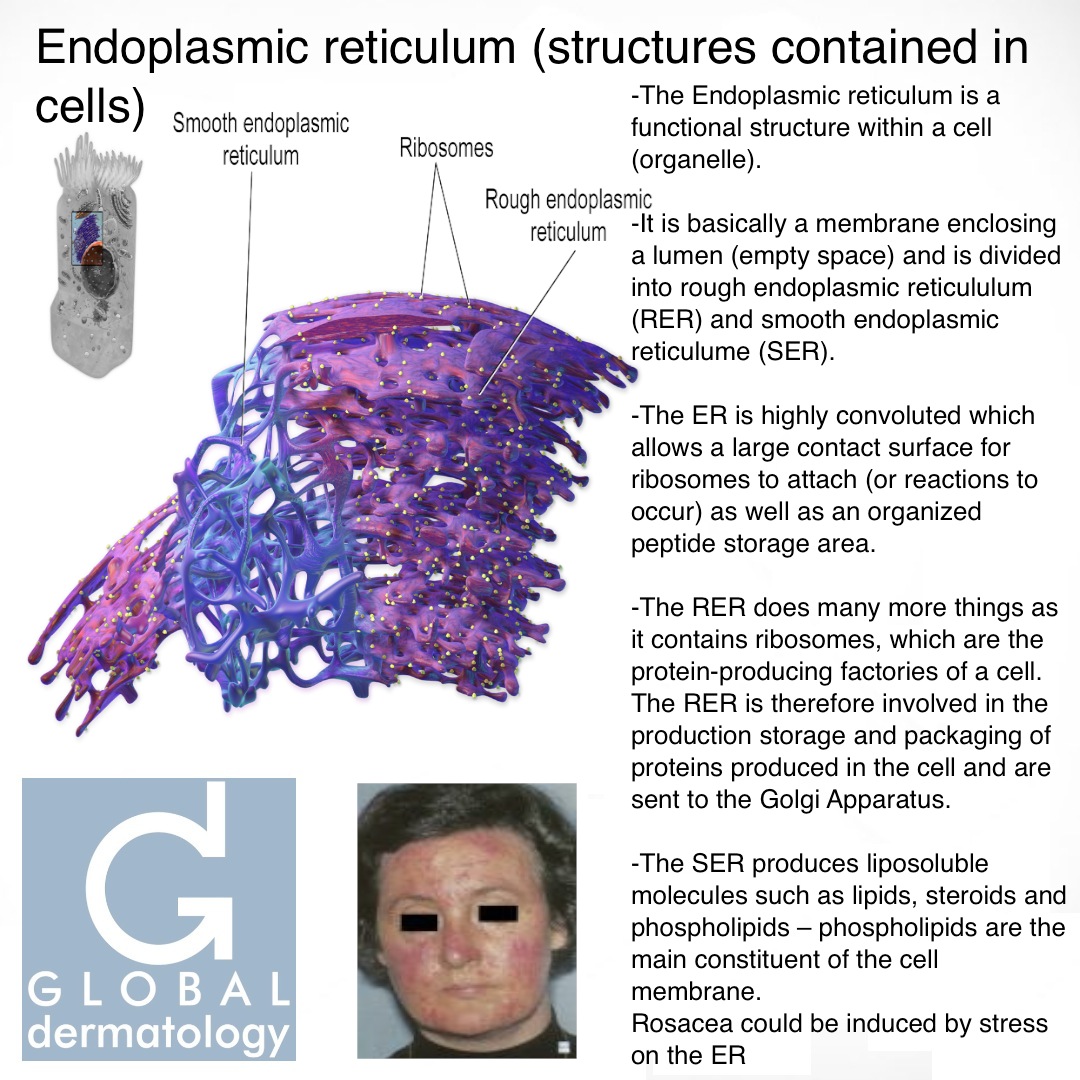
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a large organelle made of membranous sheets and tubules that begin near the nucleus and extend across the cell. The endoplasmic reticulum creates, packages, and secretes many of the products created by a cell. Ribosomes, which create proteins, line a portion of the endoplasmic reticulum. Endoplasmic Reticulum The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a large, dynamic structure that serves many roles in the cell including calcium storage, protein synthesis and lipid metabolism. Recent work on several different human diseases has highlighted a role for several different ER-shaping proteins in diverse diseases such as Alzheimer's and Hereditary Spastic