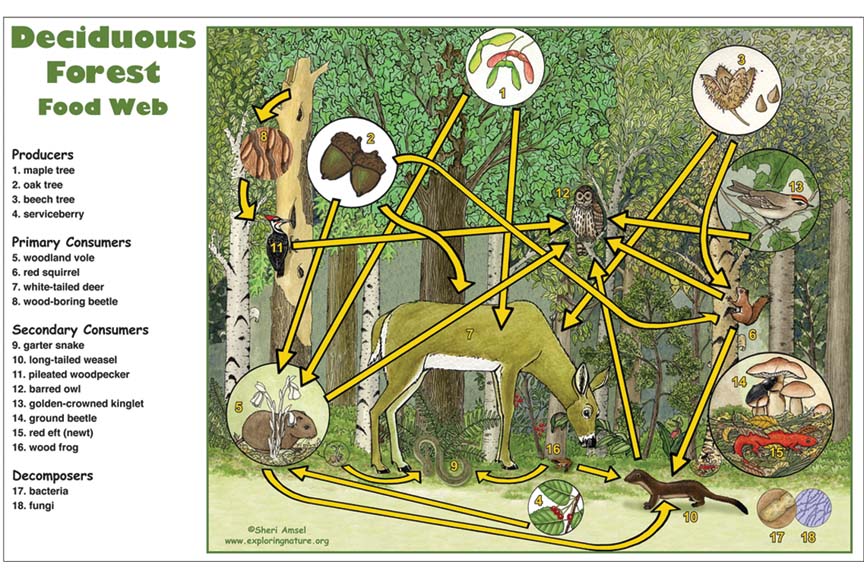
Deciduous Forest Food Web Activity Biology Diagrams Learn about the trophic levels and organisms in the deciduous forest biome, a type of temperate forest with rich biodiversity and seasonal changes. See a simple diagram of the food web and how producers, consumers, and decomposers interact in this ecosystem. Learn about the different trophic levels and organisms in the food web of the deciduous forest. See how plants, animals and decomposers interact and depend on each other in this ecosystem.
64 pages : 27 cm Explains what food webs are, and follows an American black bear, a gray wolf, a great horned owl, a Canada lynx, and a bald eagle as they weave food webs in a North American temperate forest. Includes descriptions and photographs of various temperate forest plants and animals Includes bibliographical references (pages 61-62) and index

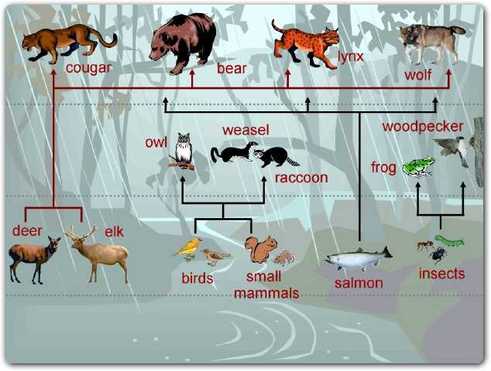
Temperate Forest Food Web: Interconnected Trophic Levels Biology Diagrams
The Producers The producers of food in a deciduous forest are the trees and plants that convert sunlight to mass and stored energy. These plants subsequently become the basic food source for the consumers above them in the food chain: for example, insects, birds, rodents and deer eat the leaves and other parts of the plants, taking on their stored energy as sustenance. However, symbiosis also

Learn how energy transfers between species in a temperate forest food web. See examples of producers, consumers, and decomposers, and compare food webs and food chains.
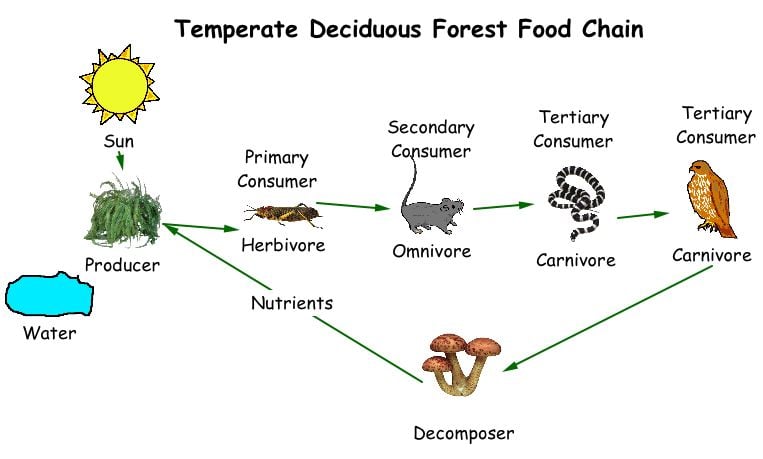
Temperate Deciduous Forest Food Web Structure Biology Diagrams
A food web in a temperate deciduous forest is a complex network of interconnected food chains that involve the transfer of energy and nutrients among different species.

In a temperate forest, trees, shrubs, and vegetation initiate the food chain as producers through photosynthesis. Herbivores like deer consume these plants, while carnivores such as wolves prey on herbivores. The interconnectedness of this food chain fosters ecological balance. However, disruptions in any level, through factors like overpopulation or habitat loss, can destabilize the ecosystem