Cell cycle checkpoint pathways impinging upon the cell division cycle Biology Diagrams Cell cycle, mitotic entry, and DNA-damage checkpoints - Arne Lindqvist's Group We are interested in how human cells decide to divide, the signalling regulating mitotic entry and its interplay with DNA-damage checkpoints.

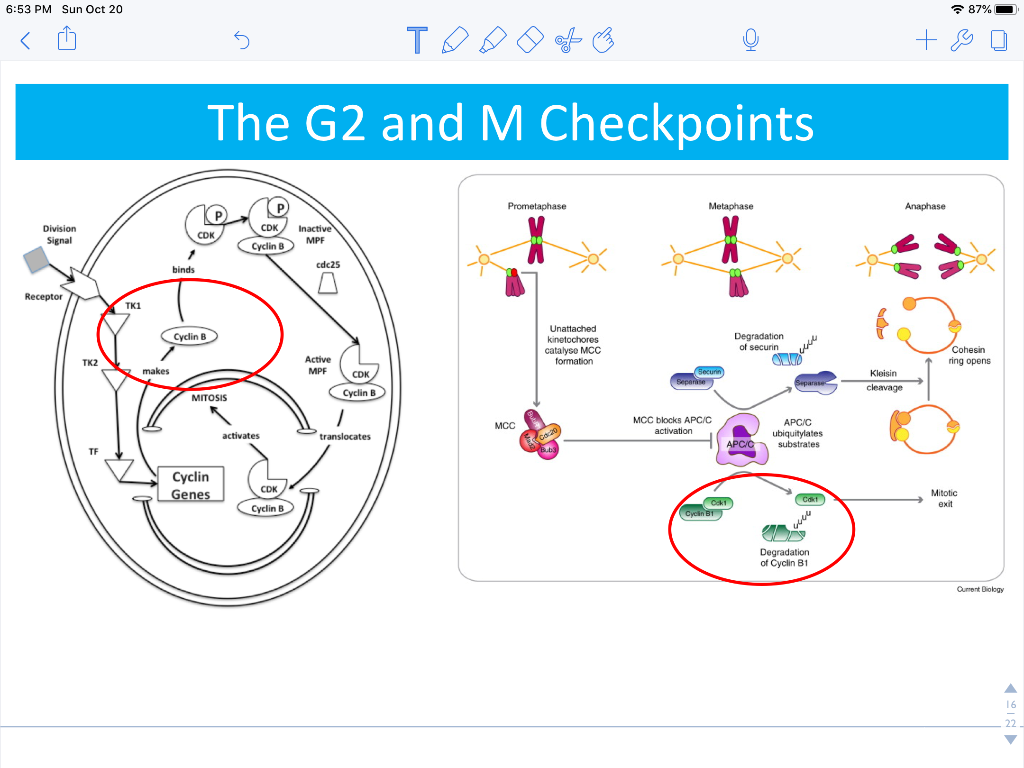
The G 2 Checkpoint The G 2 checkpoint bars entry into the mitotic phase if certain conditions are not met. As at the G 1 checkpoint, cell size and protein reserves are assessed. However, the most important role of the G 2 checkpoint is to ensure that all of the chromosomes have been replicated and that the replicated DNA is not damaged. This prevents CDK1-cyclin B activation, blocking mitotic entry until repairs are made. During mitosis, the spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC) ensures chromosomes are properly attached to the mitotic spindle before anaphase. The G 2 Checkpoint The G 2 checkpoint bars entry into the mitotic phase if certain conditions are not met. As at the G 1 checkpoint, cell size and protein reserves are assessed. However, the most important role of the G 2 checkpoint is to ensure that all of the chromosomes have been replicated and that the replicated DNA is not damaged.
Cell cycle, mitotic entry, and DNA Biology Diagrams
How cells ensure that they enter mitosis after completing replication of their genome is not fully resolved. Sobkowiak et al. describe a checkpoint involving REV7. This checkpoint has mechanistic similarities to the spindle anaphase checkpoint mediated by MAD2, a protein structurally related to REV7. In addition, the antephase checkpoint (green box) plays an important role in preventing mitotic entry in the presence of various stress conditions (see text). Of late, interest has been gathering around a checkpoint that is presumably present in antephase and delays entry into mitosis. That is, nuclei undergoing S phase could delay mitotic entry of a G2 nucleus, whereas mitotic cells stimulated nuclei to prematurely enter mitosis. In addition, studies in oocytes had determined a similar relationship between S phase and mitosis [9, 10].

Keywords: mitosis, checkpoint, DNA damage, chromosome segregation, aneuploidy 1. Introduction Exit from mitosis is the final cell cycle transition, which represents the completion of mitosis and the entry into a new interphase.

Regulation of Mitotic Exit by Cell Cycle Checkpoints: Lessons From Biology Diagrams
Cells carry Mad2-GFP to record checkpoint activation, and Clb2-mCherry to record both mitotic entry (Clb2 rise time) and mitotic exit (Clb2 degradation time). Length of mitotic arrest is defined as the difference between mitotic exit and mitotic entry. The mechanisms by which mitotic entry is prevented in response to DNA damage are similar to those in the G1/S checkpoint. DNA damage triggers the activation of the aforementioned ATM/ATR pathway, in which ATM/ATR phosphorylate and activate the Chk1/Chk2 checkpoint kinases.
